|
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Home - Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/APA-Title-Main.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
|||||||||||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance and Network Centric Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/isr-ncw.png) |
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||||||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Updated: Mon Jan 27 11:18:09 UTC 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian/Soviet/WarPac
Ground Based ECM Systems Technical Report APA-TR-2009-0501 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| by
Dr Carlo Kopp, AFAIAA, SMIEEE, PEng May 2009 Updated June, 2009 Updated April, 2012 Text, Line Art © 2009 - 2012 Carlo Kopp |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
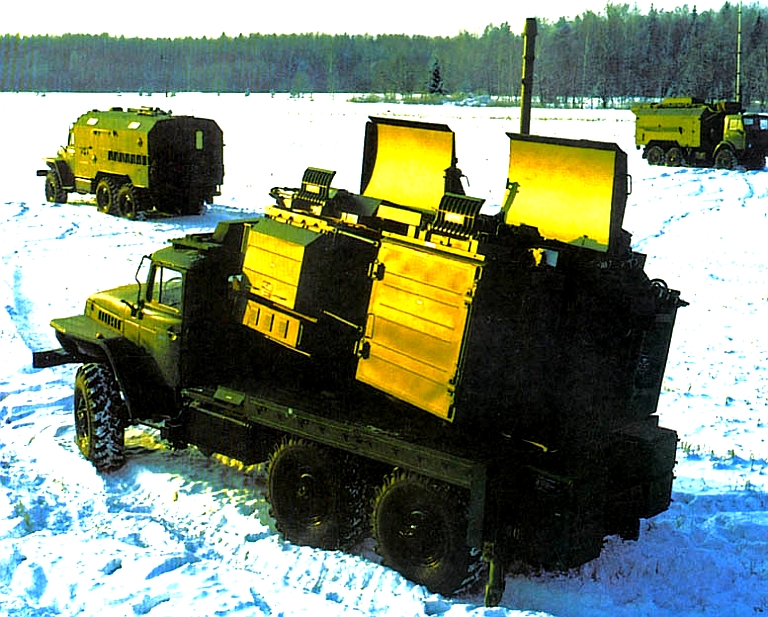
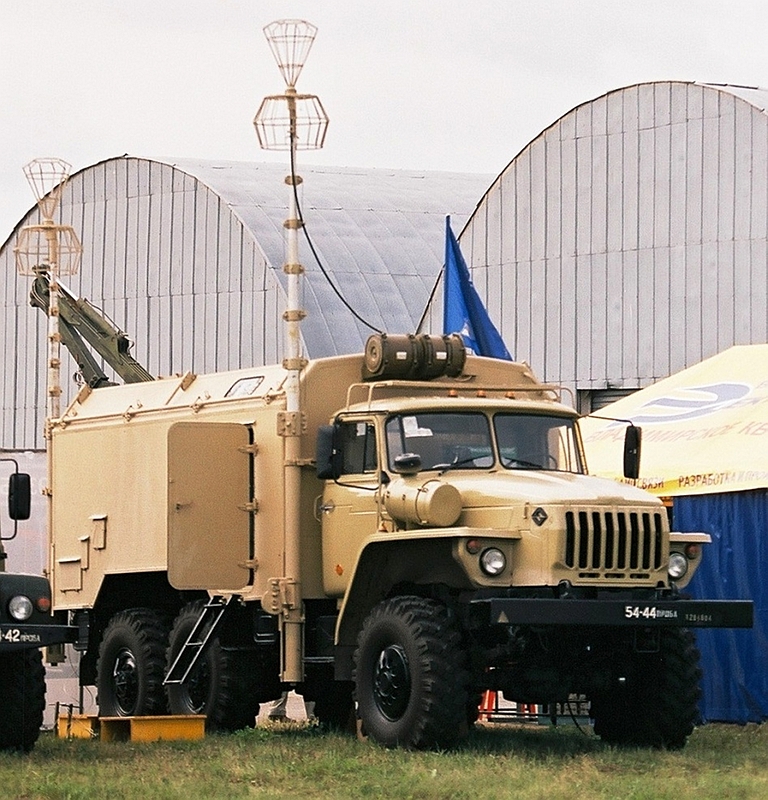
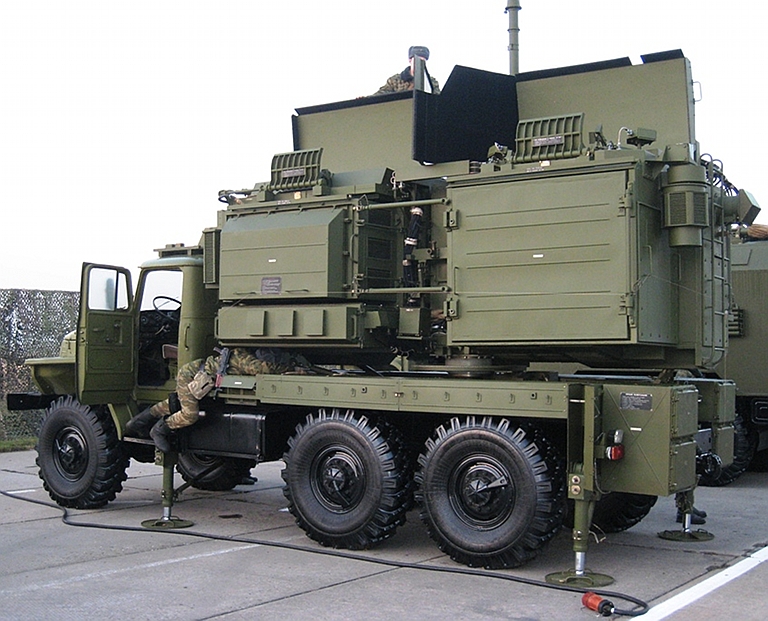 The Kvant SPN-2,3,4
Heart Ache family of mobile jammers are designed to deny surveillance
using radars in the 2 to 4 centimetre wavelength bands, with additional
capabilities against terrain following and terrain avoidance radars
operating in the same bands (Images © Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IntroductionRussia's defence industry
continues to actively export a wide range of ground based electronic
countermeasures systems, spanning both communications jammers and radar
jammers, the latter mostly optimised for the defeat of airborne ISR
systems.
Due to the technically sensitive nature of EW, public disclosures on the technical parameters of these designs are often limited. With the availability of GaAs components, DRFM technology, and COTS processing, we can expect to see deep upgrades to a number of these systems in coming years. 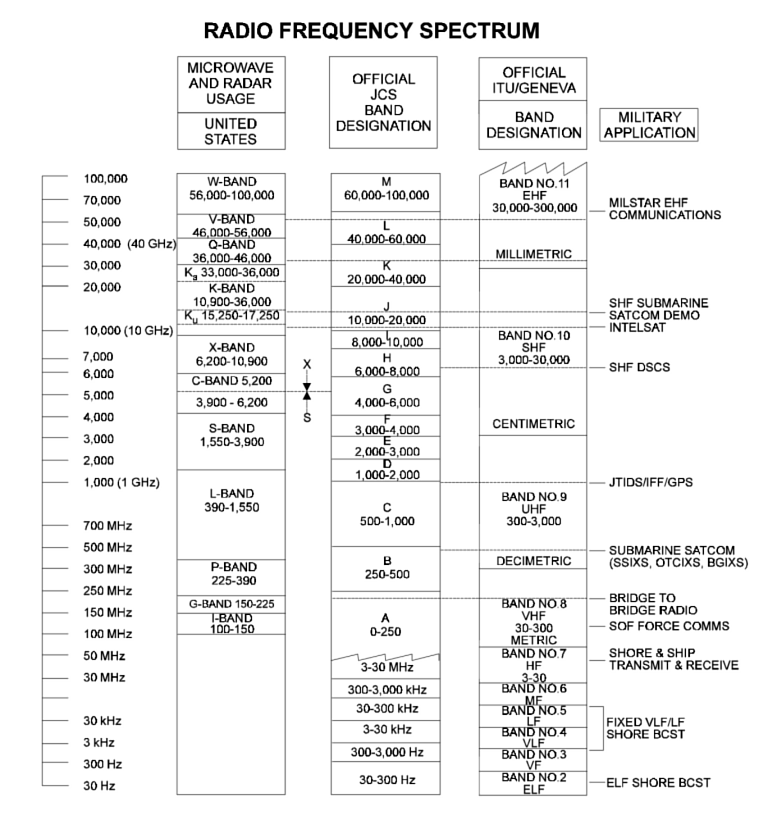 US
DoD Frequency Chart.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronic CounterMeasures Systems | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
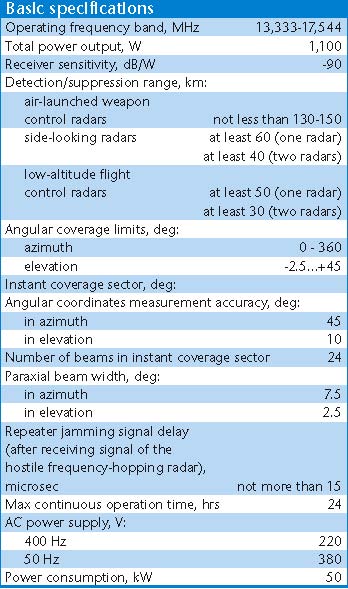
Kvant SPN-3 / 1RL248-3 High Power X-Band Radar JammerTarget Emitters: SLARs, Attack Radars The SPN-3 Heart Ache is a derivative of the
Ku-band SPN-2 jammer, built to operate
in the 3 centimetre band. The systems share a considerable amount of
hardware, but
differ in the RF components of the designs. Cited band coverage is 8.5
to 10.2 GHz[3].
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
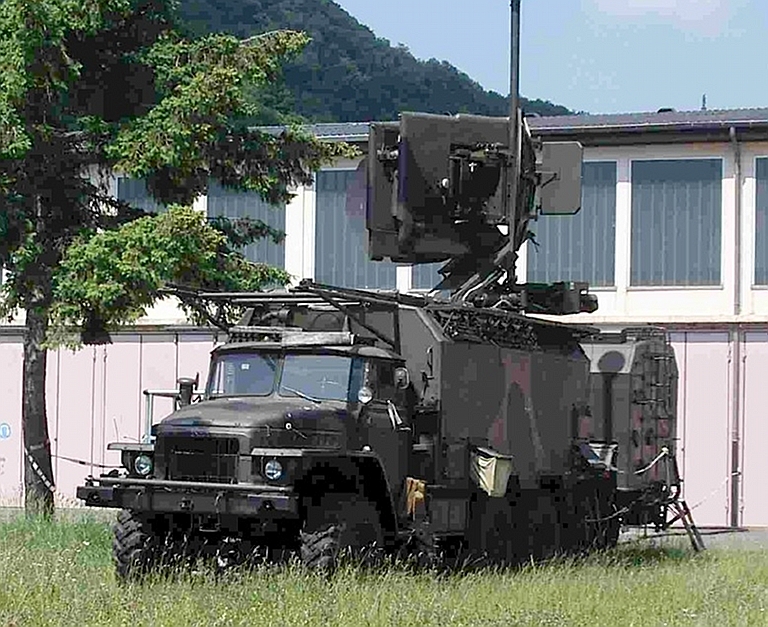
Kvant SPN-4 / 1RL248-4 High Power X-Band Radar Jammer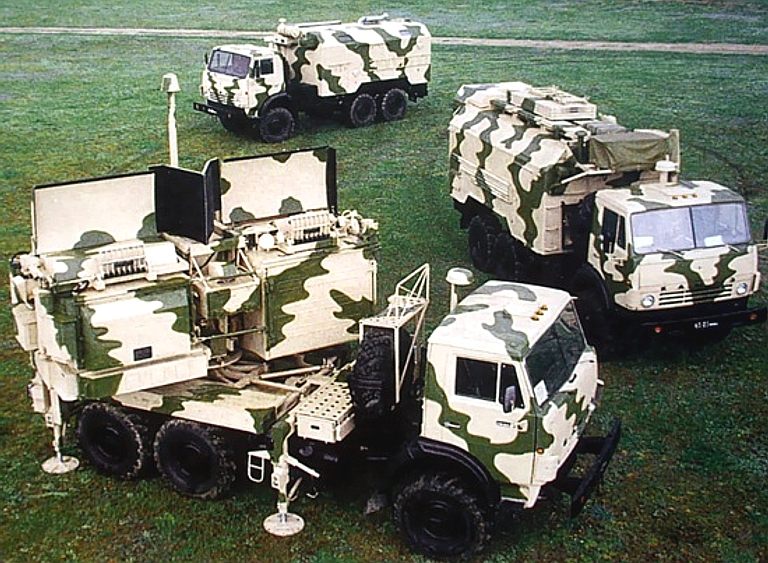 Target
Emitters: SLARs, Attack
Radars
The SPN-4 Heart Ache is a derivative of the Ku-band SPN-2 jammer, built to operate in the 4 centimetre band. The systems share a considerable amount of hardware, but differ in the RF components of the designs. Cited band coverage is 6.0 to 8.5 GHz.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SPN-30 High Power X-Band Radar Jammer Target Emitters: SLARs, Attack Radars, TFRs Rosoboronexport Description (Cite): The upgraded SPN-30 Paint Box
noise
jamming system is designed to deny enemy
reconnaissance and observation of area and small-size ground objects by
airborne side-looking radars (SLAR/SAR), air-to-surface fire control
radars, as well as navigation and low-altitude terrain following radars.
The SPN-30 system provides the following modes:
  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
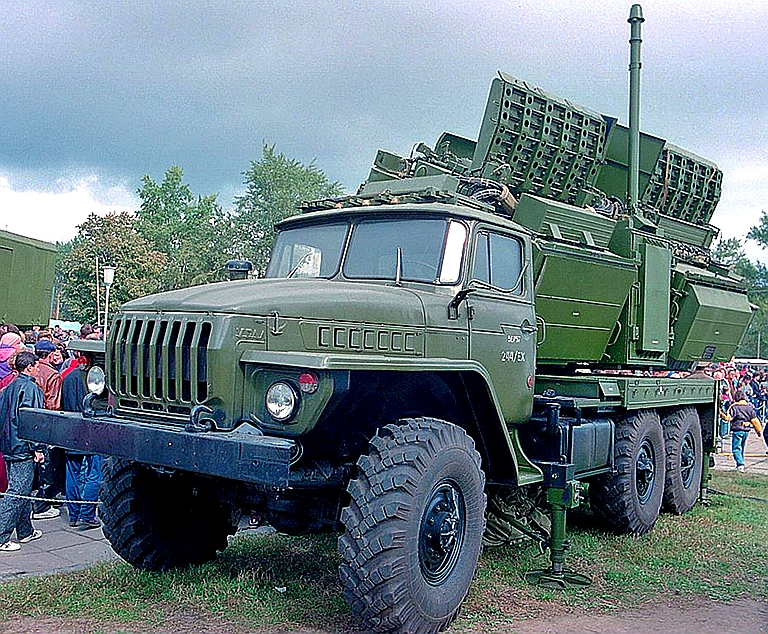
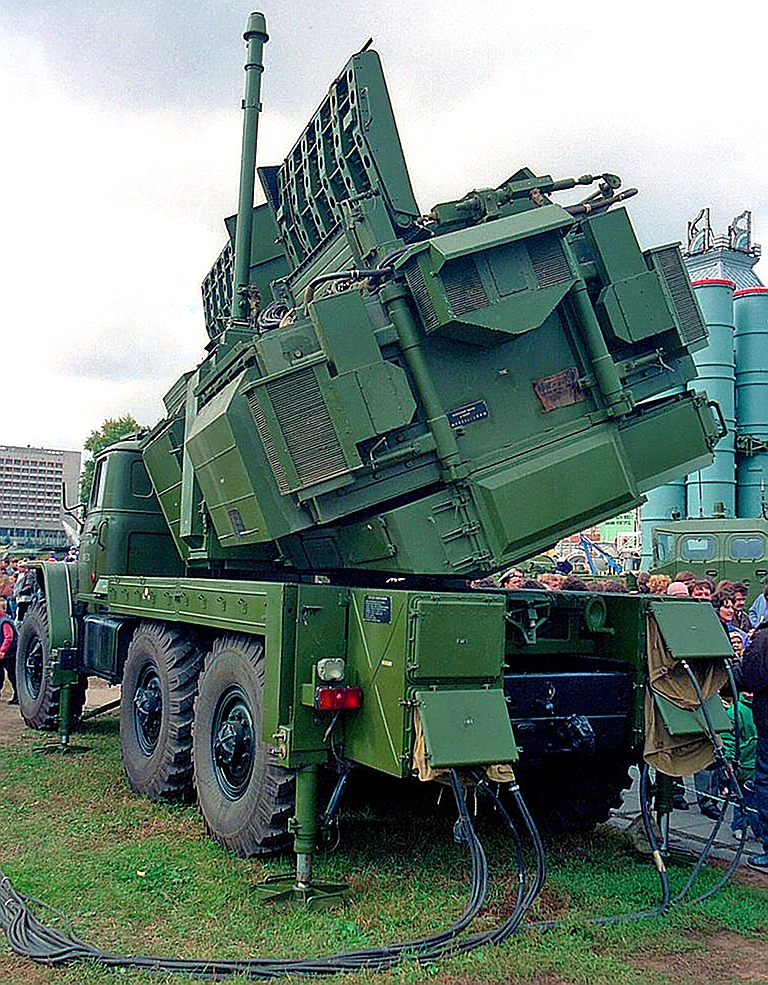
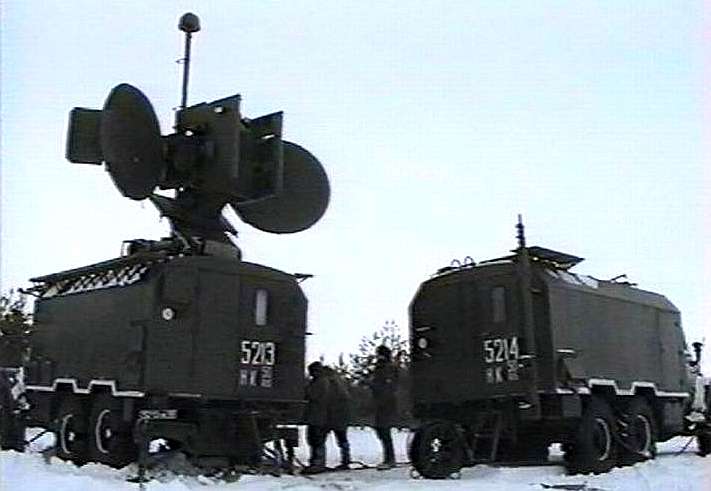
Kvant SPN-40/SPN-40M2 / 1RL238 High Power Ku-Band Radar Jammer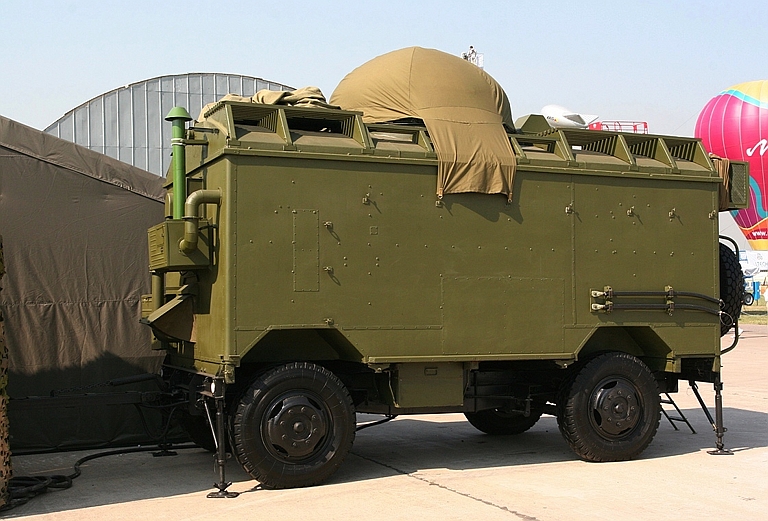 Target
Emitters: SLARs, Attack
Radars, TFRs
The SPN-40 Dog Cart was specifically developed as a Ku-band noise and deception jammer intended to defeat NATO fighter bomber Terrain Following Radars (Tornado / F-111), but also other airborne emitters operating in the same Ku-band.
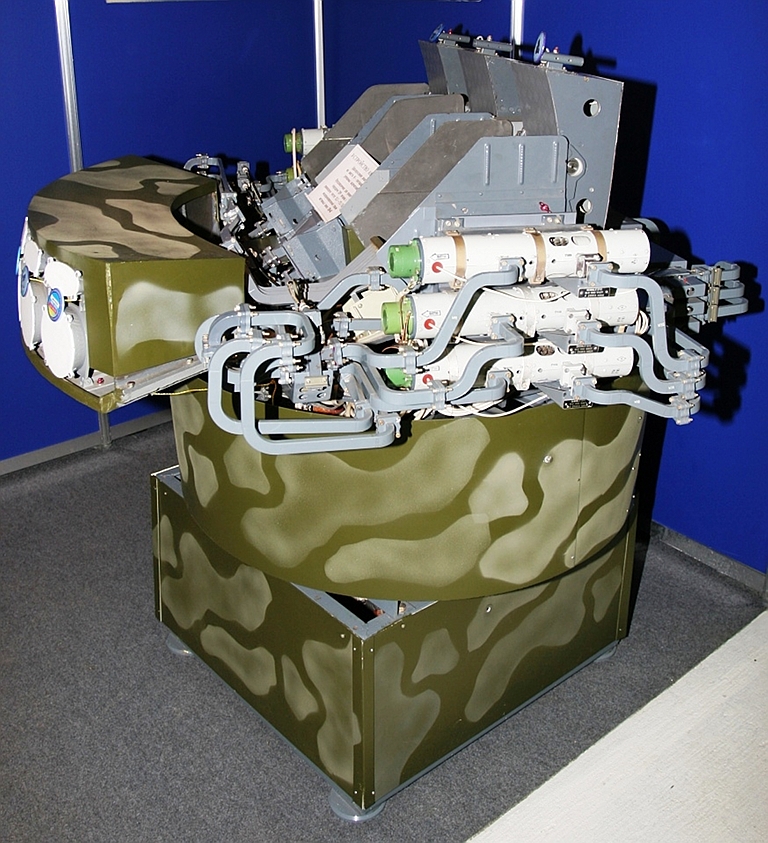 Above:
SPN-40M2 upgraded
steerable emitter array, below: poster image of SPN-40M2 stowed for
redeployment (image © Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
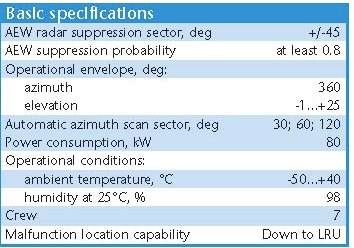
Pelena-1 High Power S-Band Counter-AWACS Radar Jammer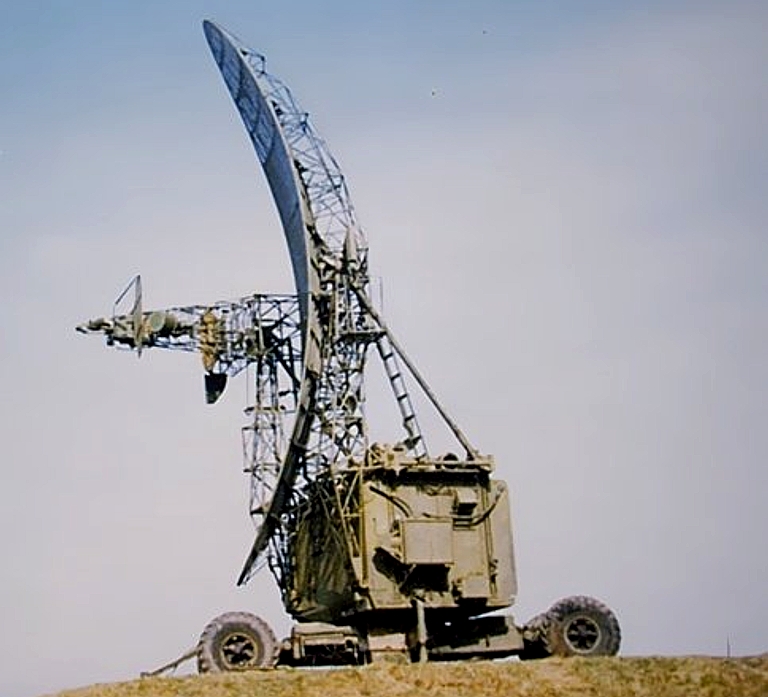 Target Emitters: APY-1/APY-2 E-3 AWACS Rosoboronexport Description (Cite): The Pelena-1 jamming system is
designed to jam airborne
early warning radars of AWACS-type aircraft.
The system denies detection by AEW radars of the protected installations with radar cross-sections of up to 15 sq.m. It is effective at a range of 50-80 km from installations protected and up to 250 km from radars being jammed.
 Pelena-6 Communications Jammer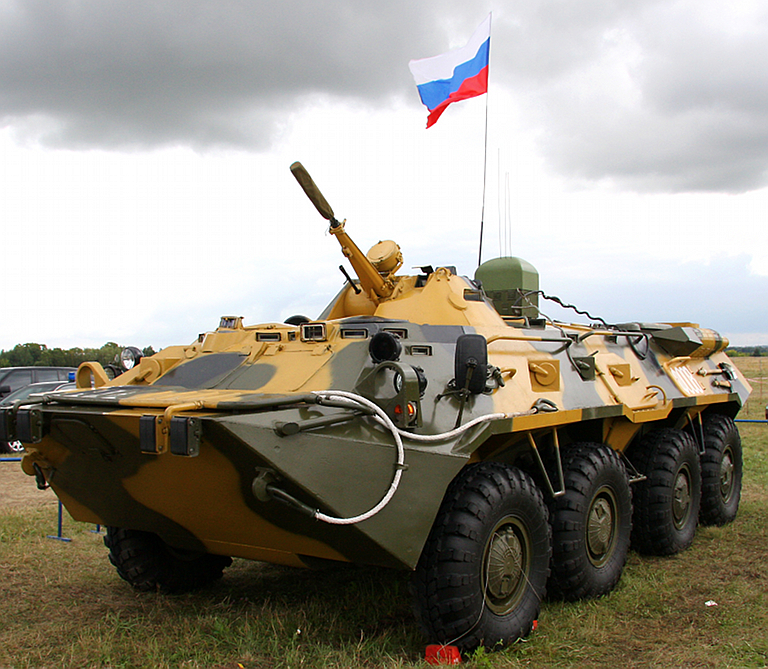 Pelena 6 jammer installed on a BTR-70 IFV chassis at MAKS 2009 (© 2009 Vitaliy V. Kuzmin).  A
range of frequencies 20 - 1000 МГц 20 - 1000
MHz
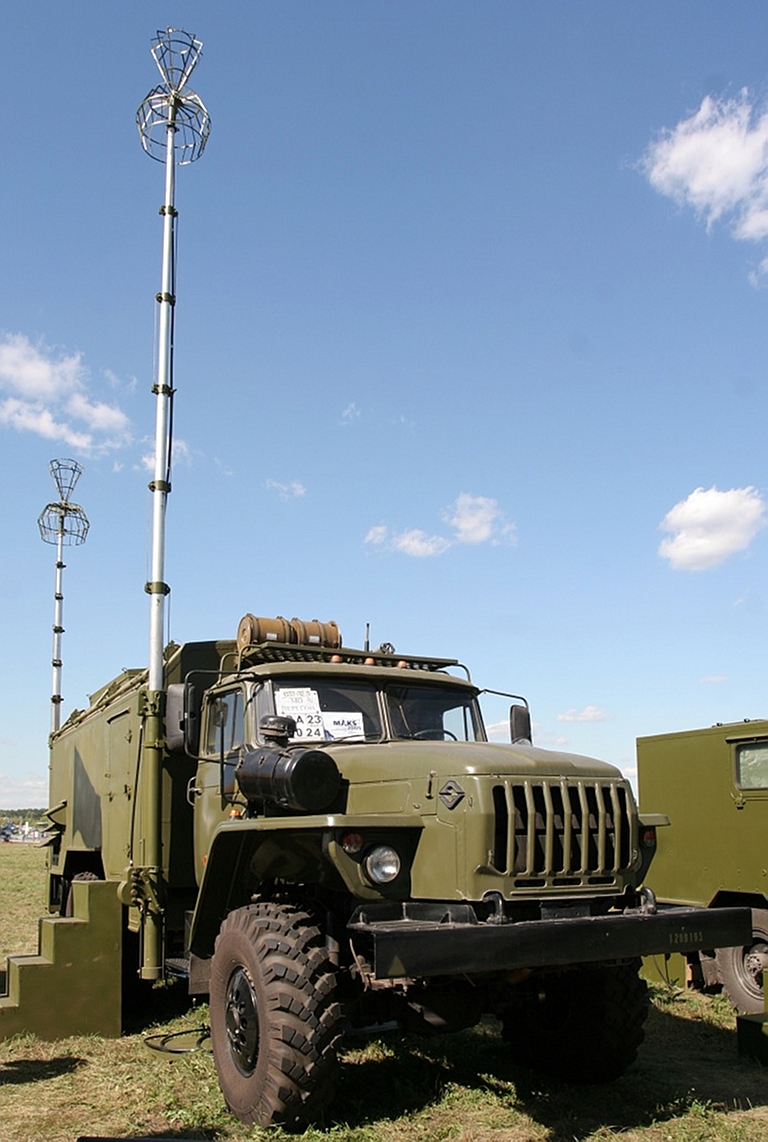
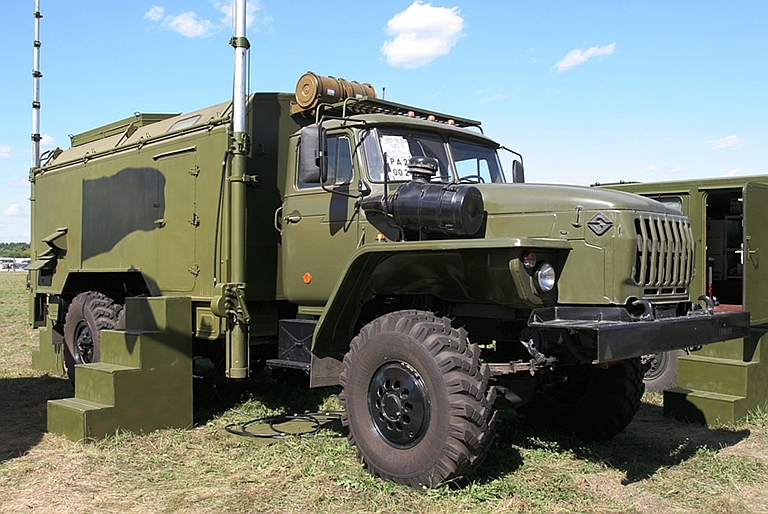
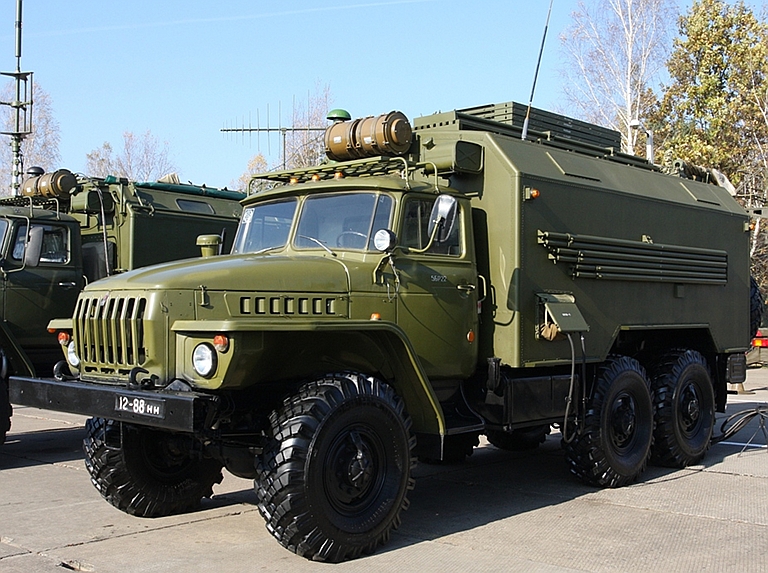
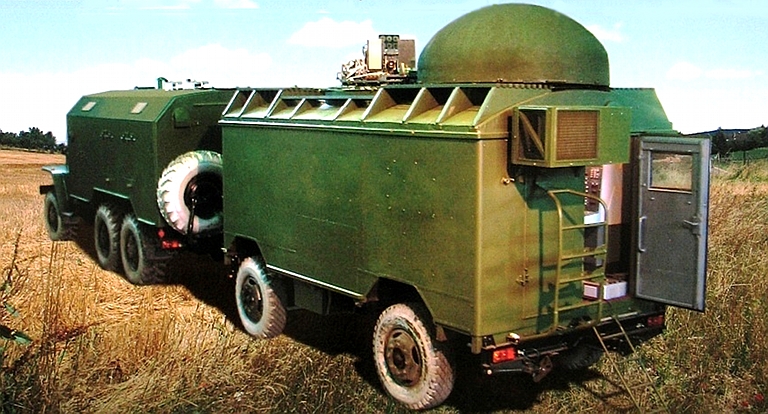
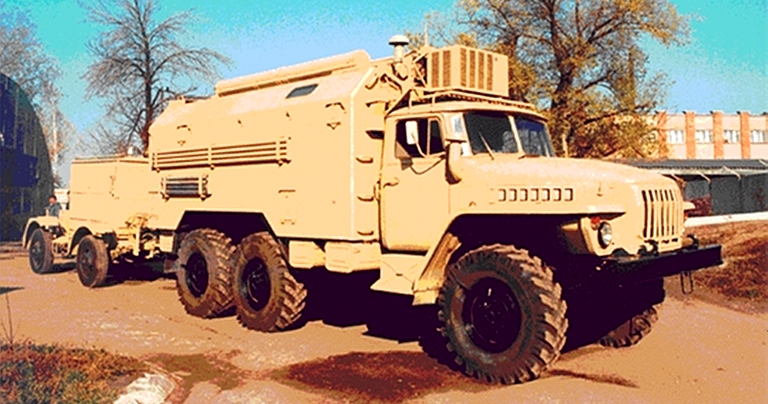
Выходная мощность Power Output не менее 60 Вт not less than 60 W Количество литер Number Liter 4 4 Вес передающего устройства Weight transmitting device не более 18 кг. not more than 18 kg. Конструктивное исполнение Embodiment Специальный металлический корпус с дополнительными кронштейнами для крепления штатного бронижелета с целью защиты изделия в боевых условиях. Special metal housing with additional bracket for mounting a full-bronizheleta to protect products in combat conditions. Габаритные размеры Dimensions 380х290х270 мм. 380h290h270 mm. Электропитание от бортсети Power of bortseti 12(+3; -1,2) В или 24 (+6, -2,4) В. 12 (3, -1,2) or 24 (+6, -2.4) V. Потребляемая мощность Power не более 450 Вт not more than 450 W  Signal Topol E High Power UHF-Band Counter-AEW&C Radar Jammer
Target
Emitters: APS-120/125/138/139/145
E-2C Hawkeye
Manufactured by the Signal Stavropol Radio Plant, the Topol E is a specialised Counter-ISR jammer developed to defeat variants of the US Navy E-2C Hawkeye AEW&C system. Two subtypes are available, intended to defeat various configurations of the E-2 series: Variant 1: Effective against the AN/APS-120,-125,-138,-139 radars; Variant 2: Effective against the AN/APS-120,-125,-138,-139, -145 radars; Комплектация поставки НСП Станция изготавливается в двух комплектах поставки согласно таблице.
Технические характеристики
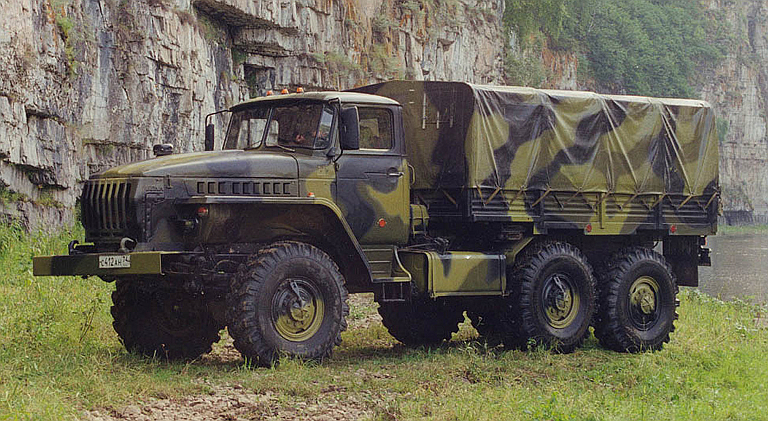 Ural 4320-21 truck used for mobile variant of Topol E jammer (Avtomobilniy Zavod Ural). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
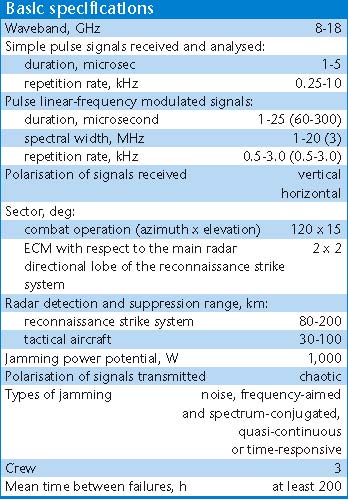
1L245 Ground-Based Weapons Control Radar Suppression System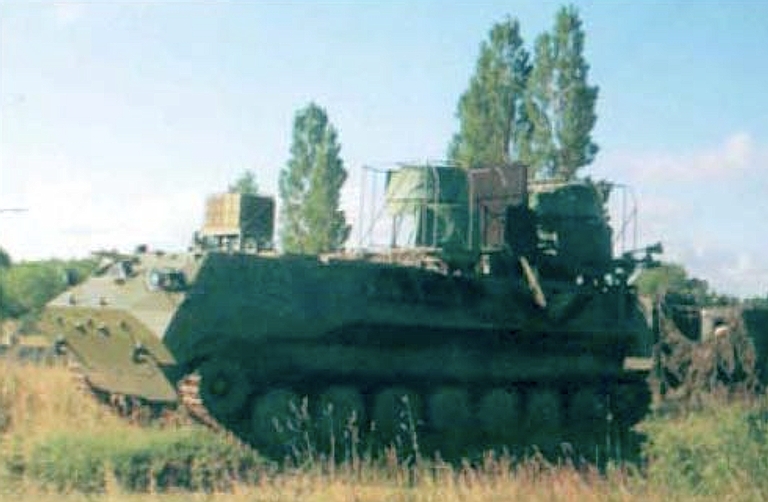 Target Emitters: Attack Radars Rosoboronexport Description (Cite): The 1L245 radar suppression
system is designed to protect friendly ground installations, weapons
and other materiel, including small-size materiel, from electronic
reconnaissance by airborne radars.
The system provides electronic suppression of the main antenna directional lobe of airborne target acquisition radars making part of reconnaissance/strike systems and operating in the terrain-mapping and moving target selection modes, as well as tactical aircraft radars including side-looking radars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
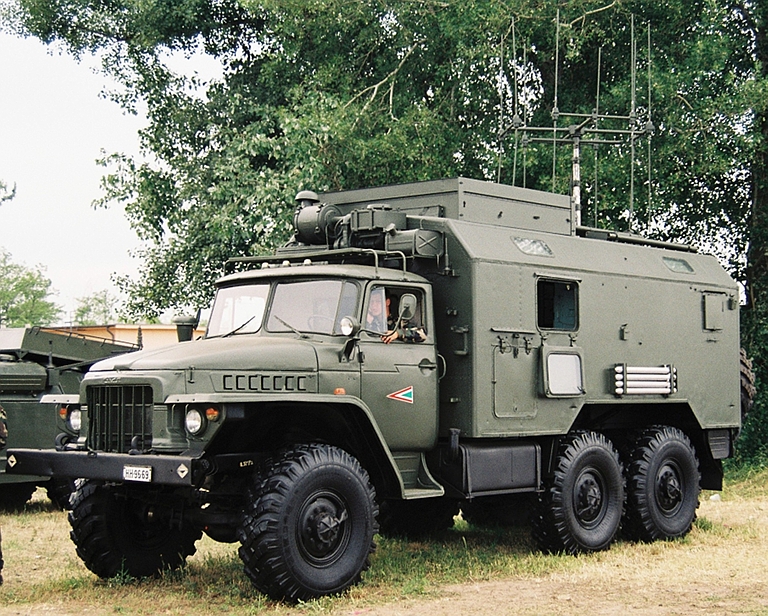
R-330B/R-330T Automated VHF Jamming System (Upgraded Version)R-330U Automated VHF Jamming System
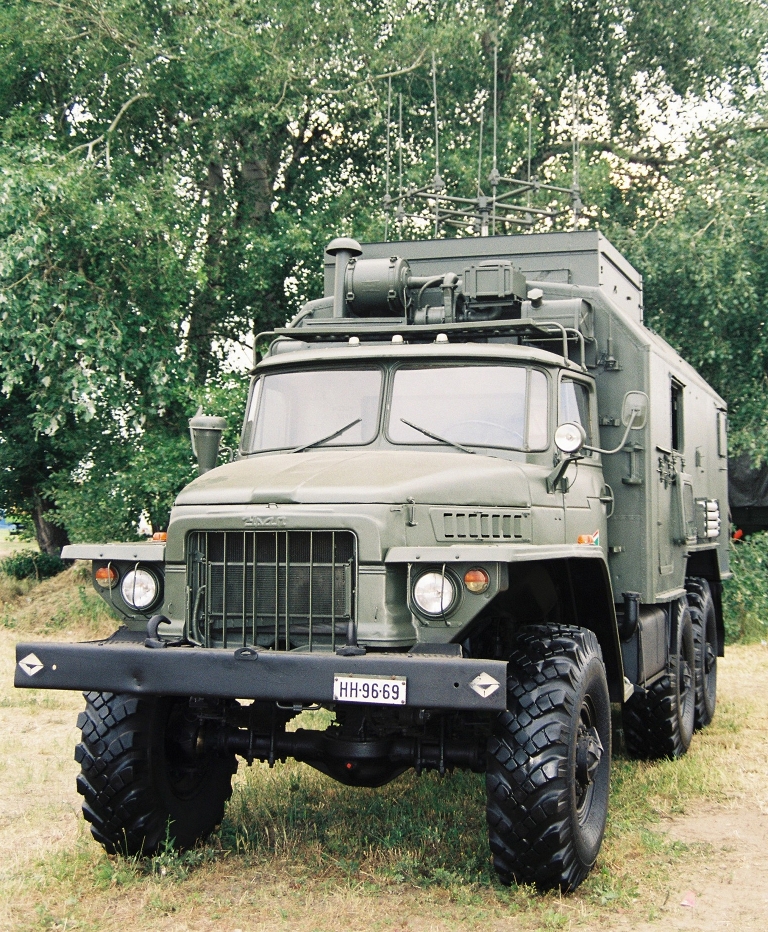 Partially deployed antenna on a Hungarian
Army R-330U jammer, carried on a Ural 375 truck. The rectangular
housing is used to stow the antenna (image © Miroslav
Gyűrösi).
Target
Emitters: VHF band
communications 30 - 60 MHz (U); 30 - 100 MHz (T/B) against AM, FM, CW,
SSB, ISB, FSK, PSK modulations.
The R-330U family of 1 kiloWatt
VHF band communications jammers was developed by TNIIR Efir. The design
operates in two subbands, 30 - 42 MHz and 42 - 60 MHz, with the
upgraded R-300T/B variants extended to 100 MHz. Older variants were
supplied on the Ural 375 chassis, newer wheeled variants on the KAMAZ
43101 or Ural 43203-31 / К2-4320 6 x 6 chassis, with the MTLBu tracked
variant also remaining on offer. The system is powered either by a
towed ED-30 (ЭД30-Т400-1РПМ1) diesel generator or mains grid power
converter.
Rosoboronexport Description (Cite): The upgraded R-330B/R-330T VHF
jamming system is designed for detection, direction-finding and jamming
of VHF communication facilities operated at tactical command level at
fixed frequencies with conventional waveforms, in programmed and
automatic frequency tuning modes, as well as for transmitting short
encoded messages. The jamming system provides analysis and selection of
emitters’ signal parameters.
Composition The R-330B/R-330T VHF jamming system consists of an equipment vehicle on a wheeled (R-330T) or tracked (R-330B) chassis, a diesel electric power station mounted on a two-axle trailer (R-330T), or MT-Lbu armoured tracked chassis (R-330B), a set of operational documentation, and a single spare parts, tools and accessories set. 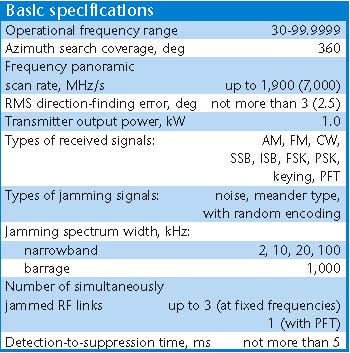
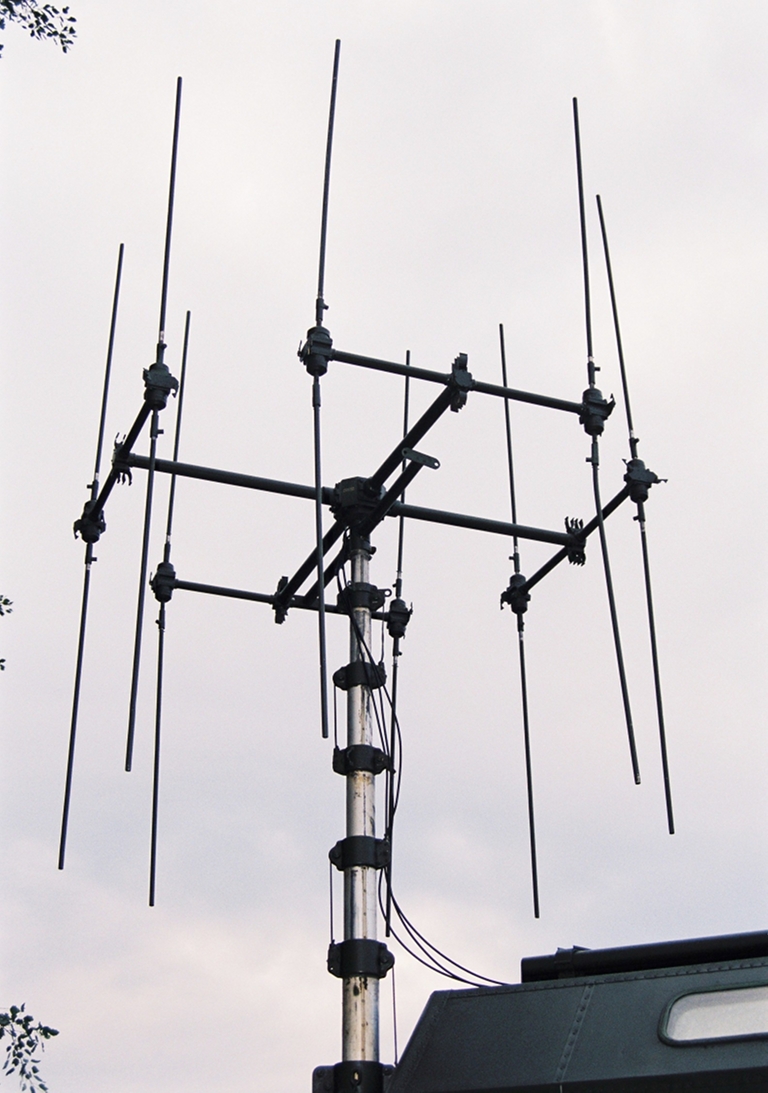
 New
build R-330T hosted on the
Ural 43203-31 / К2-4320 6 x 6 chassis, stowed with generator in tow,
and deployed (Efir images).
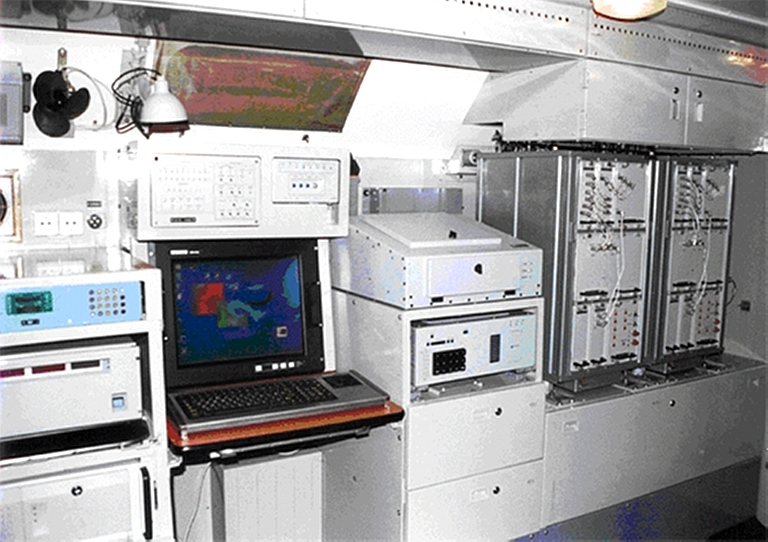  New build R-330T interior. The COTS
digital hardware displaces the hardwired analogue components of the
legacy R-330U series (Efir images).
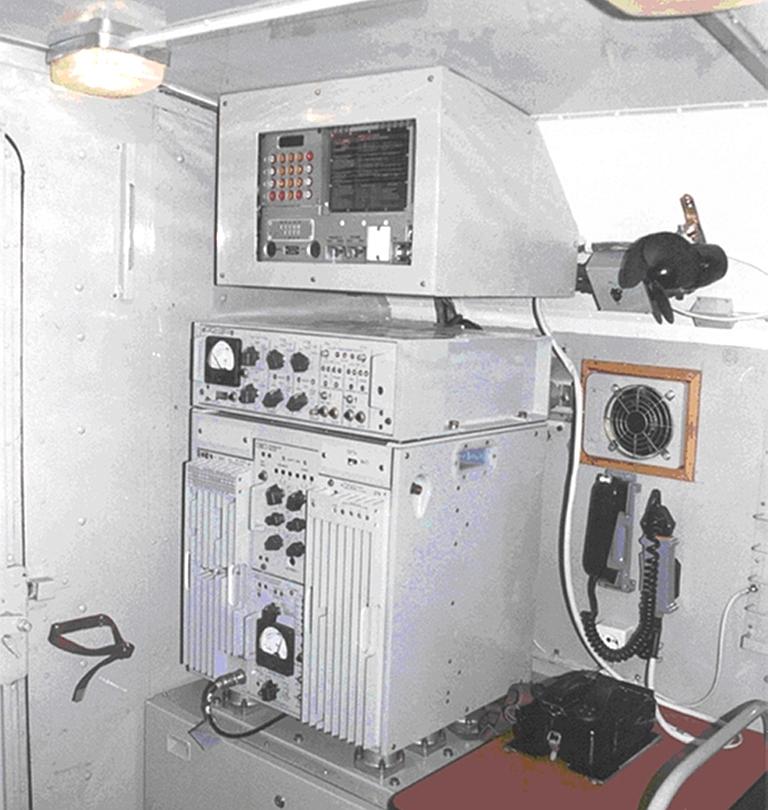 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
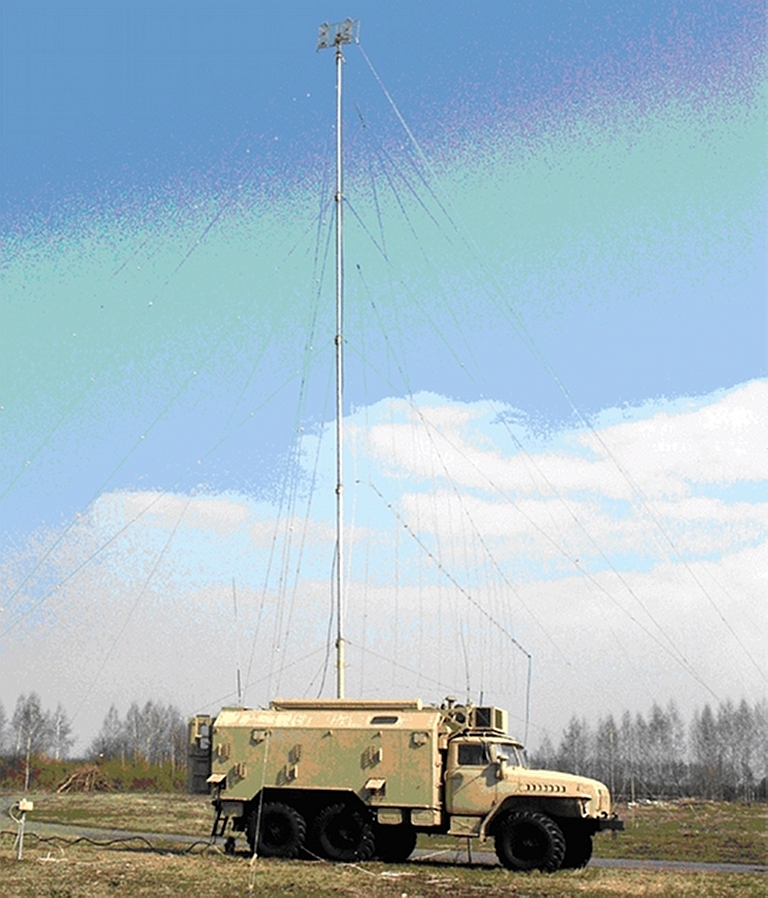
R-934B/BM VHF/UHF Aircraft Communications Automatic Jamming StationThe R-934B jammer is intended
to disrupt airborne voice and data communications channels operating in
the VHF and UHF bands. The system is available in two configurations,
either carried on an MT-LBU tracked chassis, or a Ural 4320-31 series 6
x 6 truck with a K1-4320 chassis, using a 16 kW towed generator.
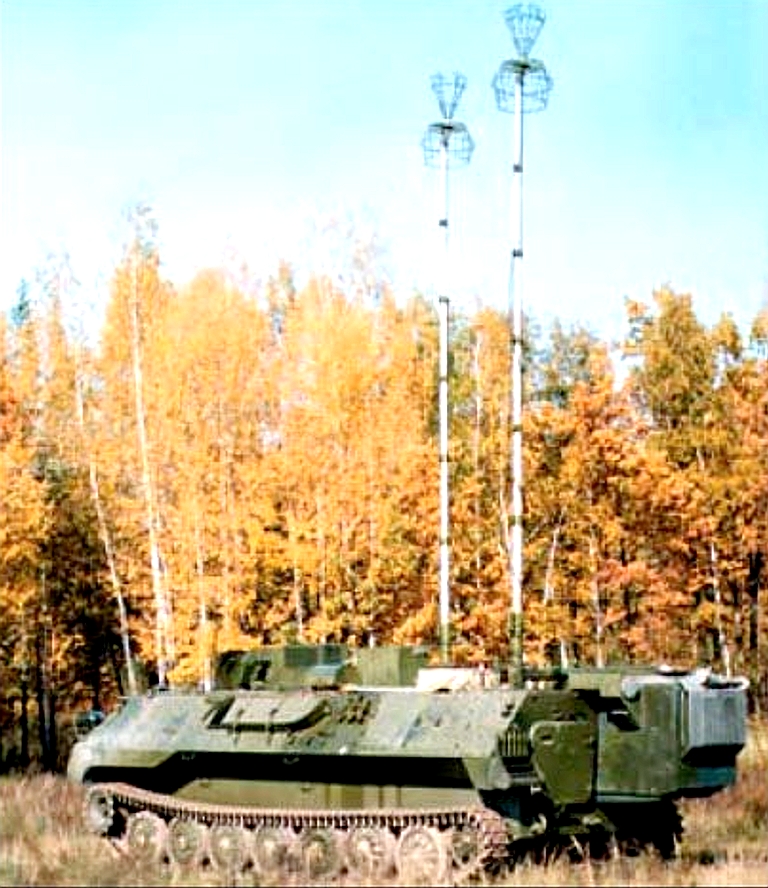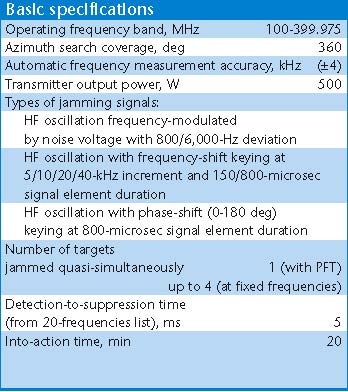  R-934B jammer carried on the MT-LBU tracked chassis.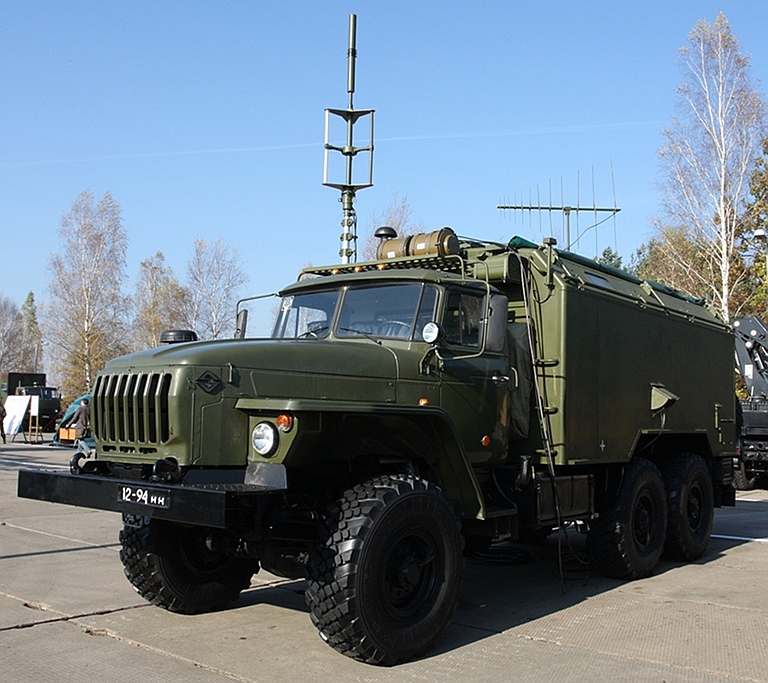  A
stowed R-934B system.
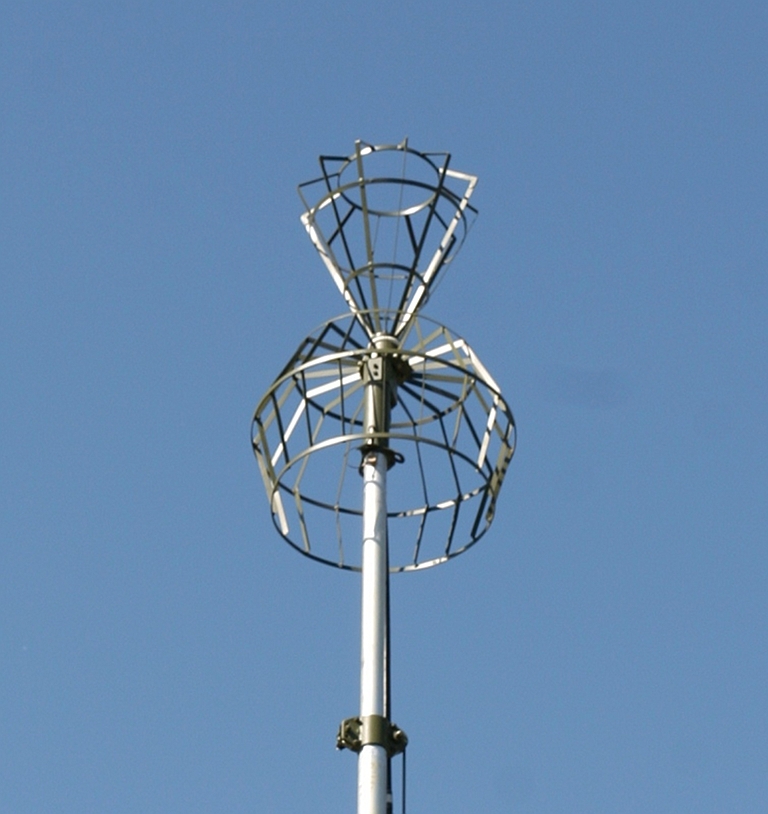 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronic
Warfare C3 / Command Posts |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Russian doctrine for the
operation of EW assets in air defence applications employs a centrally
controlled model. A Panorama sector
Command Post controls one or more
Kordon-60 Command Posts, each of which is tied to an 85V6 Orion/Vega
Emitter Locating System, and a group of jammers.
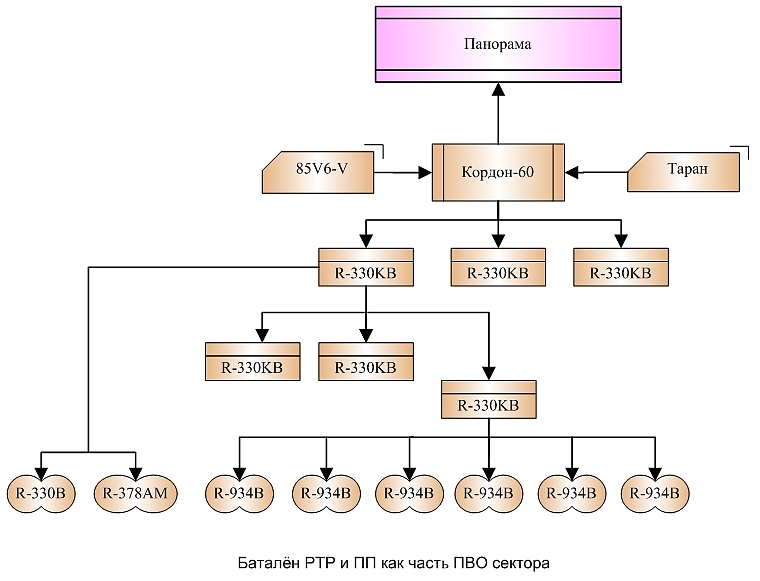 Air
defence sector ELINT and EW
battalion structure.
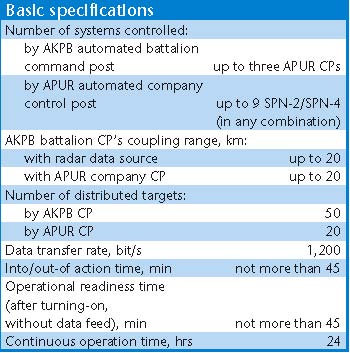
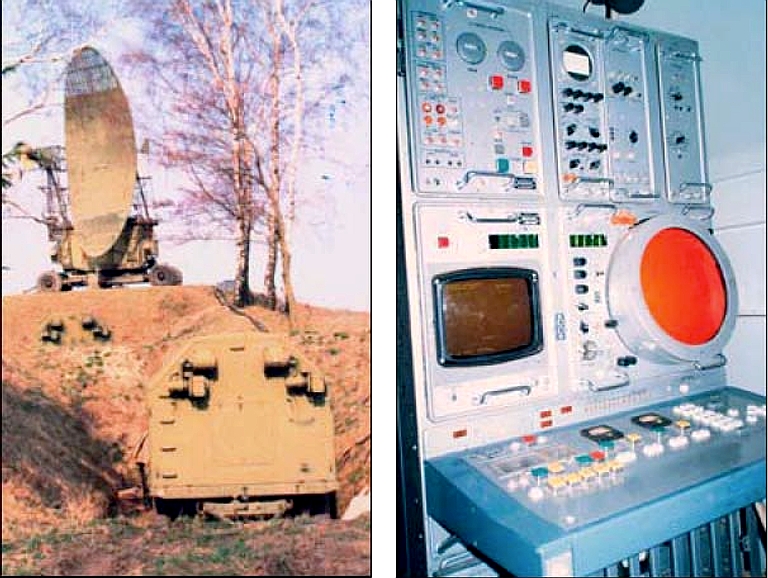
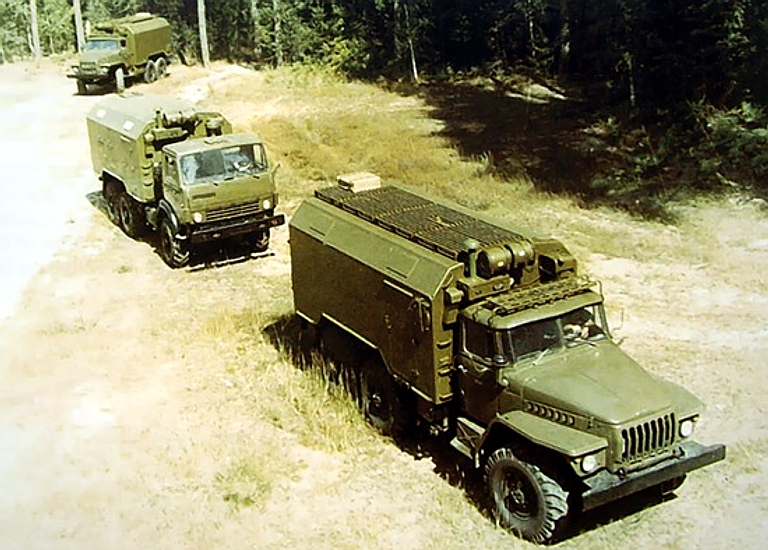
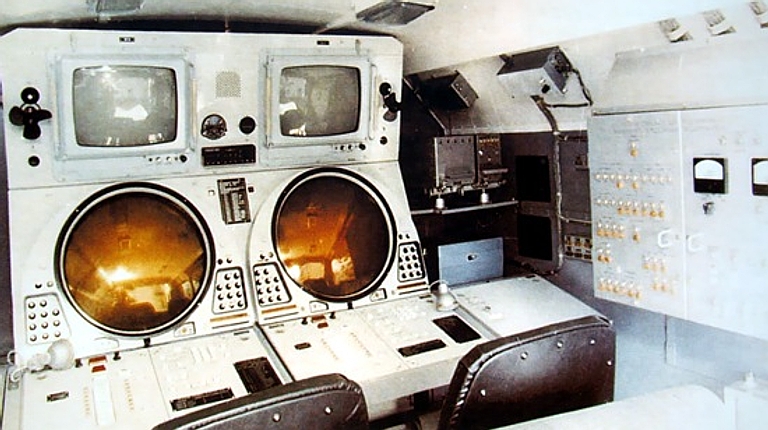
Kvant AKUP-1 / 1L213M Automated Jammer Control System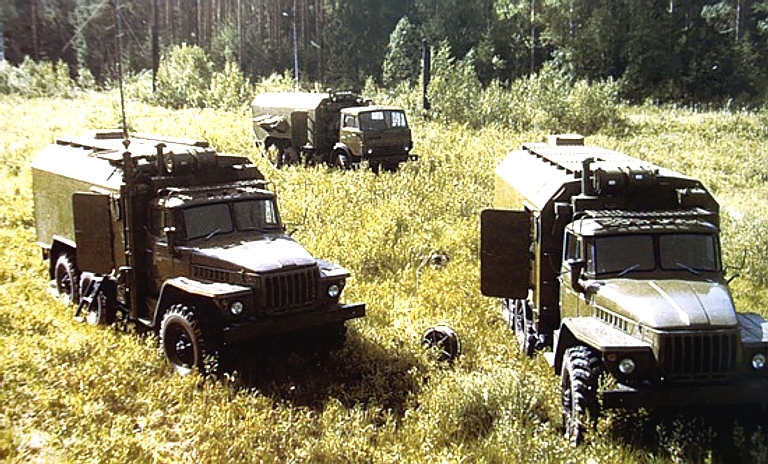 Rosoboronexport Description (Cite): The AKUP-1 (1L213M) automated
jammer control system is designed to control operation of a group of
jamming stations of three jamming companies.
Each jamming company can comprise up to nine jamming stations (six SPN-4s and three SPN-2s) and one automated control post. Composition: The AKUP-1 automated jammer
control system comprises one AKPB automated battalion command post and
three APUR automated company control post. Each post incorporates:
The jamming companies operation
is coordinated by the automated battalion command post.
The AKUP-1 jammer control system is fitted with the automatic testing and fault-finding equipment capable of tracing malfunctions to individual line replaceable units. It can operate reliably with temperatures ranging from -50oC to +40oC and relative air humidity of up to 98%. The AKPB and APUR control posts are manned with seven- and six-person crews respectively.
    References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Imagery
Sources: Kvant, Rosoboronexport, Russian MoD |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Technical Report APA-TR-2009-0501 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
|||||||||||||
| Artwork, graphic design, layout and text © 2004 - 2014 Carlo Kopp; Text © 2004 - 2014 Peter Goon; All rights reserved. Recommended browsers. Contact webmaster. Site navigation hints. Current hot topics. | |||||||||||||
|
Site Update
Status:
$Revision: 1.753 $
Site History: Notices
and
Updates / NLA Pandora Archive
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Tweet | Follow @APA_Updates | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
![F-111 Aardvark Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/f-111.png)
![F/A-18 Hornet and Super Hornet Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/fa-18a.png)
![Aerial Refuelling and Airlift Capabilities Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/aar-lift.png)
![Directed Energy Weapons and Electromagnetic Bombs Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/dew.png)
![Notices and Updates Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notices-128.png)
![APA NOTAM and Media Release Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notams-128.png)
![APA Research Activities and Policy / Technical Reports Index [Click for more ...]](APA/research-128.png)
![Search Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/search-128.png)
![Briefings and Submissions - Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/briefs-128.png)
![Air Power Australia Contacts [Click for more ...]](APA/contacts-128.png)
![Funding Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/funding-258.png)