|
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Home - Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/APA-Title-Main.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
|||||||||||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance and Network Centric Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/isr-ncw.png) |
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||||||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Updated: Mon Jan 27 11:18:09 UTC 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Soviet/Russian
Guided Bombs
Technical Report APA-TR-2009-0806 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| by
Dr Carlo Kopp August 2009 Updated April, 2012 Text © 2008 - 2012 Carlo Kopp  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
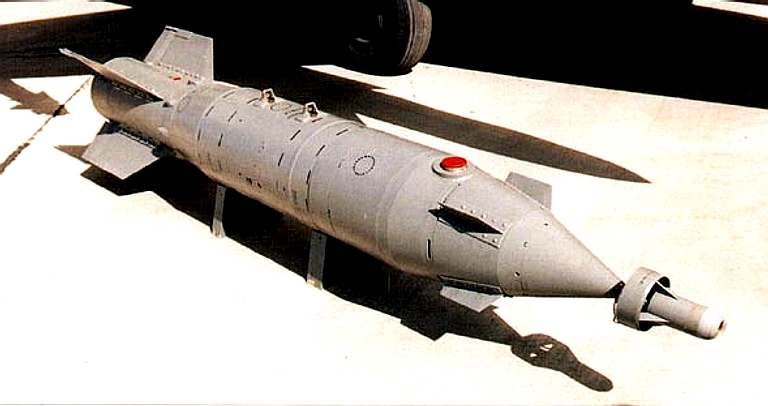
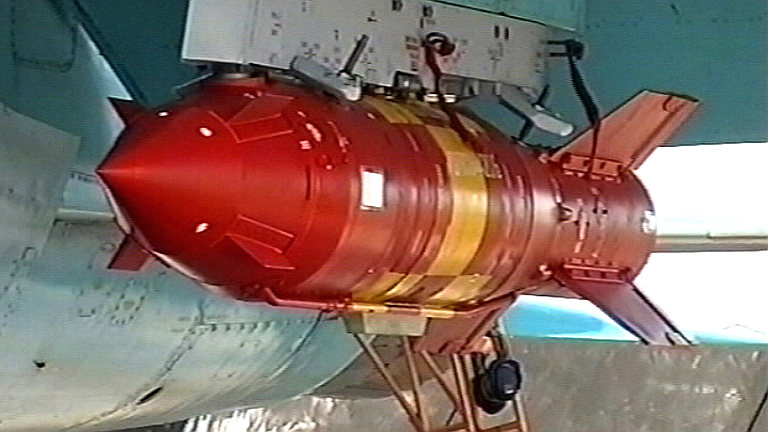
 GNPP Region KAB-500Kr-F electro-optical guided bomb. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Precision and Accurate Guided Bombs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GNPP Region KAB-1500, KAB-500 Specifications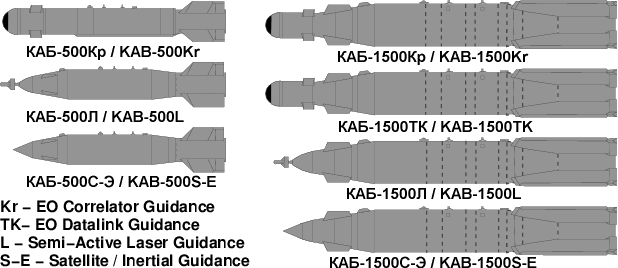
Source: Tactical Missiles
Corporation, Russia
Source: Tactical Missiles
Corporation, Russia
Source: Tactical Missiles
Corporation, Russia
 27N semi-active laser homing seeker (Rosoboronexport).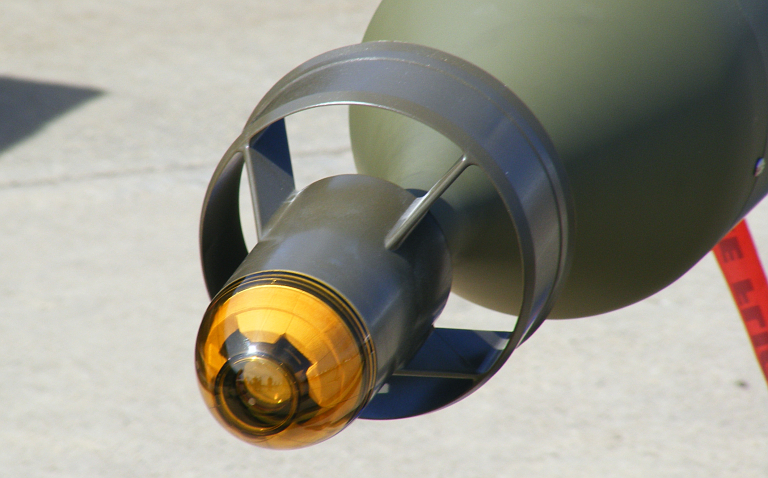  Raytheon Paveway II seeker (© 2009, Carlo Kopp).  24N1 gimballed semi-active laser homing seeker (Rosoboronexport).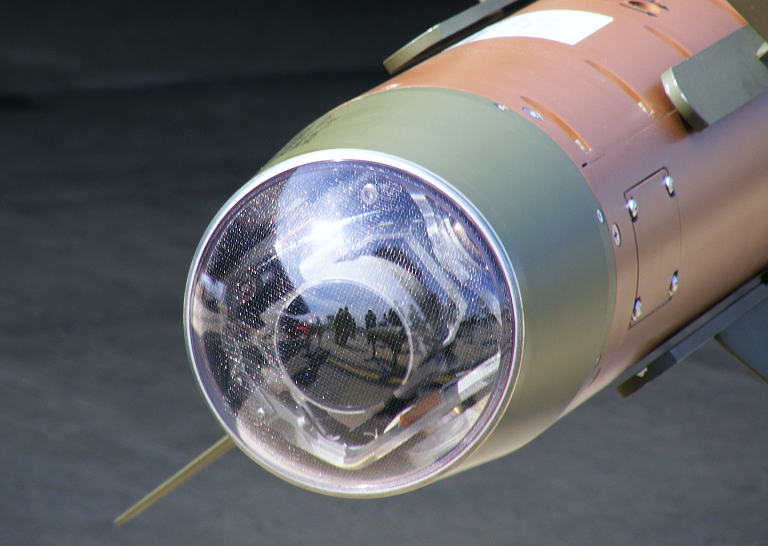  Raytheon Paveway III gimballed semi-active laser homing seeker (© 2009, Carlo Kopp). 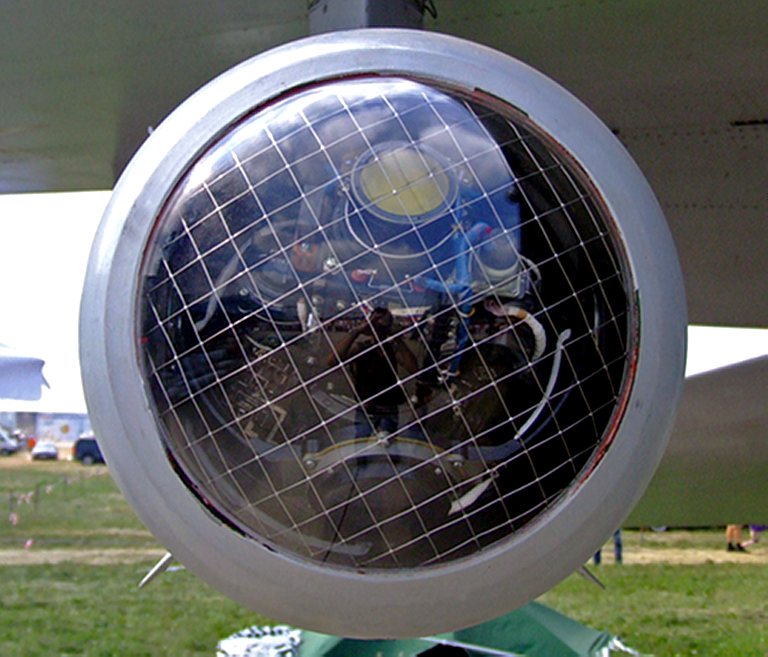 KAB-500Kr gimballed television seeker.
Note the optical interference filter coating on the imaging device, and
the large field of regard facilitating acquisition (Wikipedia image).
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-1500LG-Pr-E / KAB-1500LG-F-E / KAB-1500LG-OD-E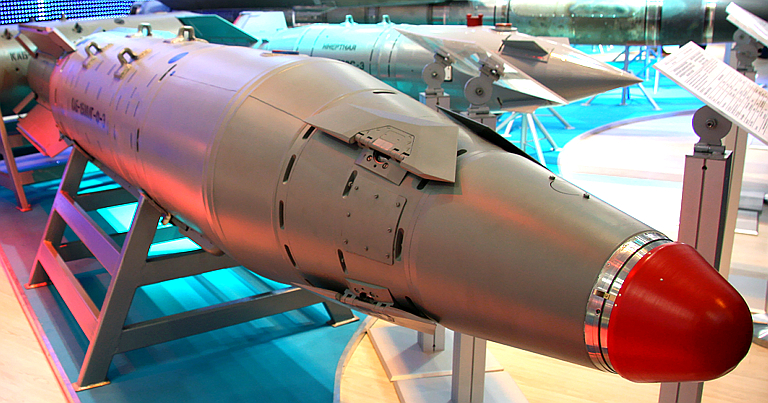 Stowed
KTRV KAB-1500LG-F-E on display at MAKS 2009 (© 2009 Vitaliy V. Kuzmin).
The new KAB-1500LG is the
enhanced laser semi-active homing 1,500 kg guided
bomb intended to improve upon the accuracy of the earlier 27N
semi-active laser homing seeker based designs.
The weapon uses a gimballed
gyro stabilised semi-active laser homing seeker and optical design
similar to the Paveway III series.
The seeker is closest in appearance to the 24N1 series used for a
number of existing laser homing missiles. It will provide similar
characteristics to the
baseline Paveway III seeker. The cited CEP is 4 to 7 metres which is
consistent with this style of seeker and the P-nav control loop
technology involved.
Delivery envelope is 1 to 8 km AGL and 550 - 1100 km/h. Variants:
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
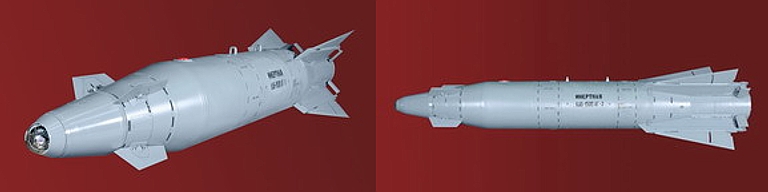
KAB-1500L-Pr-E / KAB-1500L-F-E / KAB-1500L-OD-E KAB-1500L Laser Guided Bomb with surfaces deployed. The KAB-1500L is the baseline
laser semi-active homing 1,500 kg guided bomb developed for the FA-VVS
and widely exported since the end of the Cold War. It achieved IOC in
1987.
The weapon uses the Azov 27N or later 27N1 semi-active laser homing seeker using an annular airfoil and optical design similar to the Paveway I/II series. It will provide similar characteristics to the baseline Paveway I/II seeker. The cited CEP is 7 to 10 metres which is consistent with this style of seeker and the bang-bang control loop technology involved. Delivery envelope is 1 to 15 km AGL and 550 - 1700 km/h. Variants:
 KAB-1500L
Laser Guided Bomb with surfaces stowed, on display at the Akhtubinsk Valeriy
Chkalov State Flight Test Centre open day event, September, 2005 (via
Vzlyot).
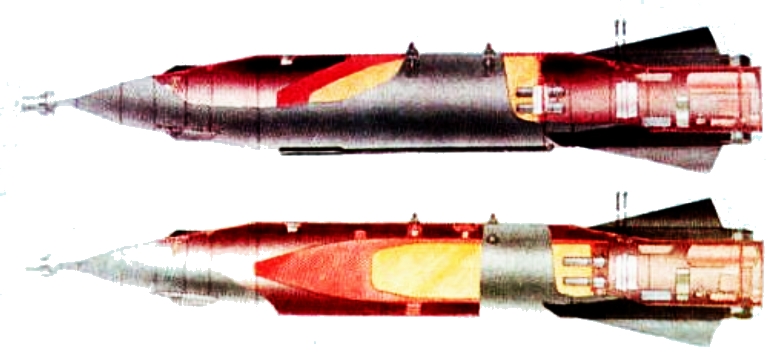 GNPP
KAB-1500L cutaways - blast/frag variant (upper) and subcalibre
penetrator variant
(lower).
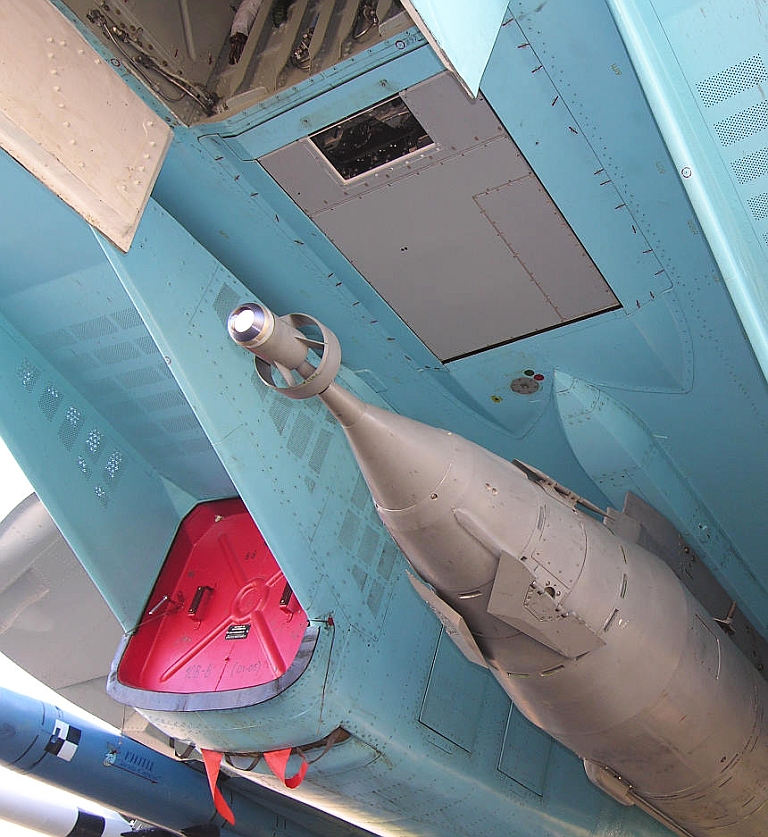 KAB-1500L-F
on the Su-34 Fullback (Russian Internet).
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-1500Kr-Pr-E / KAB-1500Kr-F-E / KAB-1500Kr-OD-E
KAB-1500Kr
Electro-Optical Guided Bomb trials round, stowed, on display at the Akhtubinsk Valeriy
Chkalov State Flight Test Centre open day event, September, 2005 (via Vzlyot).
The KAB-1500Kr series are
Electro-Optical guided bombs. The seeker employs a gimballed daylight
television imaging sensor under a wide angle glass dome. Unlike the
earlier US GBU-8 HOBOS and AGM-65 Maverick which employed contrast lock
technology, the -Kr series guidance system employs Scene Matching Area
Correlation technology more akin to the US Navy DAMASK seeker or
Tomahawk DSMAC. This results in the ability to attack low contrast
targets by exploiting the contrast of nearby terrain features or
objects.
The cited CEP is 4 to 7 metres which is consistent with this style of seeker and the P-nav control loop technology involved. The Krym series Electro-Optical seeker is built by OAO Impuls. It is limited to daylight operation. The 10 kg SU-609 guidance and control module is built by Tambovskii Elektropribor and comprises a BU-94 control unit and PG-16 gas generator. The characteristic mesh screen behind the optical window was introduced for EMC purposes and to prevent seeker jamming by RF signals. Variants:
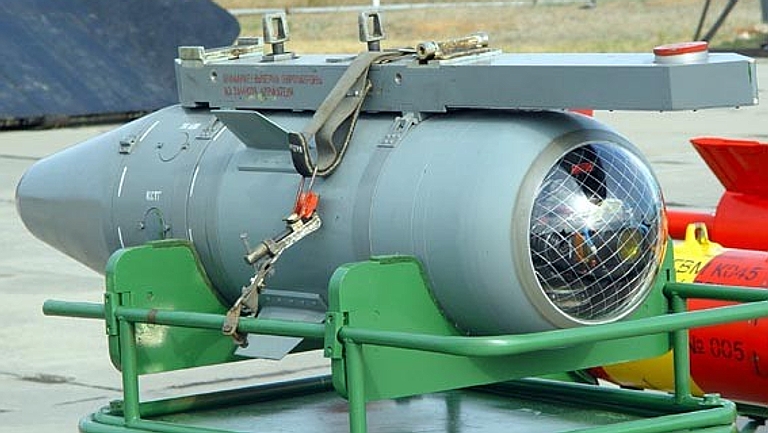 The KAB-500Kr-U is a captive carry training system for the KAB-1500Kr and KAB-500Kr guided bombs. It enables aircrew to practice acquiring and locking the bomb on targets. The unit weights 85 kg, is 1.83 m long and has a diameter of 0.35 m. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-1500TK Raduga
APK-9E Tekon datalink pod used with the KAB-1500TK variant.
The KAB-1500TK series are
Electro-Optical guided bombs with a man-in-the-loop datalink. The
seeker employs a gimballed daylight
television imaging sensor under a wide angle glass dome. The design can
be described as a fusion of ideas used in the GBU-8 and GBU-15 EO
guided bombs. The APK-9 datalink pod is used to send steering commands
to the bomb, and receive video from the seeker during flight for
display in the cockpit. This seeker will achieve similar effect to the
GBU-15 and will be extremely accurate.
The cited CEP is 4 to 7 metres
which is
consistent with this style of seeker and the P-nav control loop
technology involved.
The Krym series
Electro-Optical seeker is built by OAO Impuls. It
is limited to daylight operation. The 10 kg SU-609 guidance and control
module is built by Tambovskii Elektropribor and comprises a BU-94
control unit and PG-16 gas generator. The characteristic mesh screen
behind the optical window was introduced
for EMC purposes and to prevent seeker jamming by RF signals.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-1500S-EThe KAB-1500S-E is reported to
be a 1,500 kg satellite aided inertial
guided bomb. It is likely to use the same PSN-2001 receiver and
guidance package as the smaller KAB-500S-E.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UPAB-1500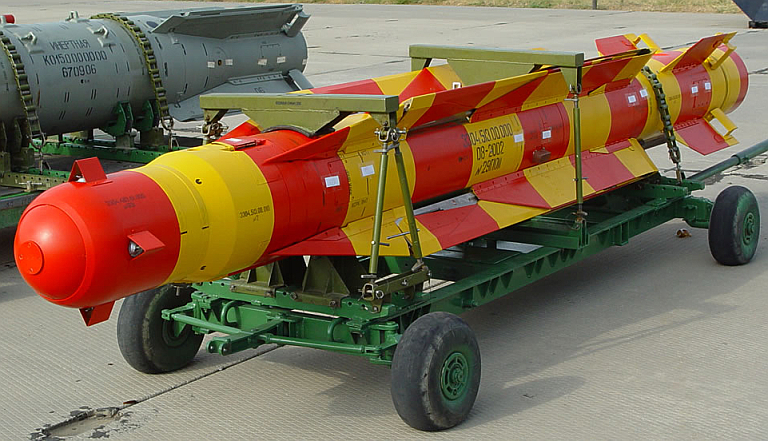 UPAB-1500Kr prototype on display at the
Akhtubinsk Valeriy Chkalov State Flight Test Centre open day event,
September, 2005 (via Russian Internet).
The UPAB-1500 (Universalnaya
Planiruyushchaya Aviatsionnaya Bomba) glidebomb was first displayed to
the public in 2005, in prototype form. Reports to date indicate that
the weapon has a glide range of 70 km for a 10 km launch altitude.
According to Russian sources cited in Russia & CIS Observer, the guidance package for the first generation of this weapon is that developed for the KAB-1500TK, comprising a EO seeker in the nose section, and a datalink transceiver in the tail to transfer seeker imagery and steering commands between the bomb and the Raduga APK-9E Tekon datalink pod carried by the launch aircraft. The latter is intended to be the Su-34 Fullback, Su-24M2 Fencer, Tu-22M3 Backfire C and Tu-160 Blackjack. As the Tekon pod has been integrated on most Su-30MK variants, the Flanker is thus also a candidate launch platform. In practical terms the guidance technique and performance makes this weapon a direct analogue to the GBU-15/EGBU-15 series but with greater glide range performance. The aerodynamic design of the
weapon is unusual, in that it employs a high aspect ratio small chord
cruciform folding wing design, unique in contemporary glidebombs. When
stowed, the cruciform main airfoils are slotted into strakes on the aft
of the weapon fuselage. Tail controls, similar to the trailing edge
design on the KAB-500/1500 tailkits, are employed.
It is intended that future variants be equipped with a range of different guidance packages, although it is likely that utility and cost will see the satellite/inertial system used most frequently. The production status of this weapon is currently unclear. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-500LG-Pr-E / KAB-500LG-F-E / KAB-500LG-OD-E / KAB-500LG-K-EThe KAB-500LG has been reported
but has yet to appear in formal product offerings. This weapon is a 500
kg semi-active laser homing design likely to employ the same gimballed
stabilised high accuracy seeker design as used in the existing
KAB-1500LG series.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-500L-Pr-E / KAB-500L-F-E /
KAB-500L-OD-E / KAB-500L-K-E
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-500Kr-Pr-E / KAB-500Kr-F-E / KAB-500Kr-OD-E / KAB-500Kr-K-E
KAB-500Kr
Electro-Optical Guided Bomb.
The KAB-500Kr series are
Electro-Optical guided bombs. The seeker
employs a gimballed daylight television imaging sensor under a wide
angle glass dome. Unlike the earlier US GBU-8 HOBOS and AGM-65 Maverick
which employed contrast lock technology, the -Kr series guidance system
employs Scene Matching Area Correlation technology more akin to the US
Navy DAMASK seeker or Tomahawk DSMAC. This results in the ability to
attack low contrast targets by exploiting the contrast of nearby
terrain features or objects. IOC was achieved in 1984.
The cited CEP is 4 to 7 metres which is consistent with this style of seeker and the P-nav control loop technology involved. The Krym series Electro-Optical seeker is built by OAO Impuls. It is limited to daylight operation. The 10 kg SU-601 guidance and control module is built by Tambovskii Elektropribor and comprises a BU-56 control unit and PG-9-2 gas generator. Variants:
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-500S-E
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-250L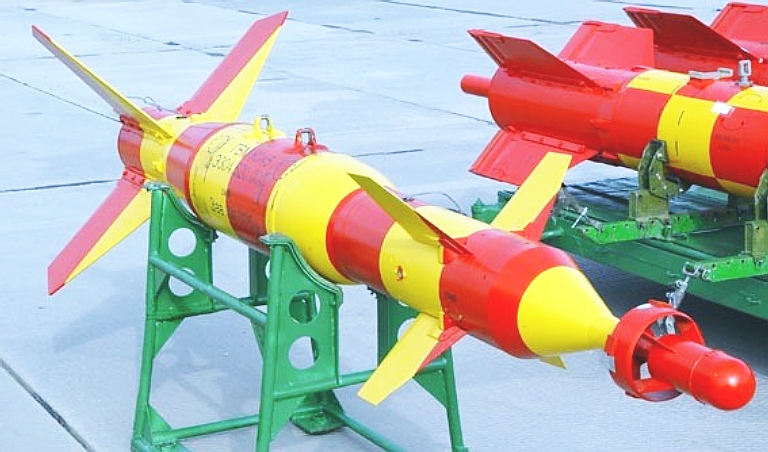 Prototype KAB-250L
laser guided bomb on display
at the Akhtubinsk Valeriy Chkalov State Flight Test Centre open day
event, September, 2005.
The KAB-250L is a
laser
semi-active homing 250 kg guided bomb. It is the smallest laser guided
bomb manufacturerd by Russian industry.
The weapon uses the Azov 27N or
later 27N1 semi-active laser homing
seeker using an annular airfoil and optical design similar to the
Paveway I/II series. It will provide similar characteristics to the
baseline Paveway I/II seeker. The cited CEP is 3 to 10 metres which is
consistent with this size of bomb, style of seeker and the bang-bang
control loop
technology involved.
Delivery envelope is 1 to 15 km AGL and 550 - 1700 km/h.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
KAB-250S-EThe KAB-250S-E is reported to
be a 250 kg satellite aided inertial
guided bomb. It is likely to use the same PSN-2001 receiver and
guidance package as the larger KAB-500S-E.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Imagery Sources: US DoD, Soviet MoD, Russian Internet Line Artwork: © 2000, 2007, 2008, 2009 Carlo Kopp Technical
Report APA-TR-2009-0806
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
![Sukhoi PAK-FA and Flanker Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/flanker.png) |
![F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/jsf.png) |
![Weapons Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/weps.png) |
![News and Media Related Material Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/media.png) |
||||||||||
![Surface to Air Missile Systems / Integrated Air Defence Systems Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/sams-iads.png) |
![Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defence Page [Click for more ...]](APA/msls-bmd.png) |
![Air Power and National Military Strategy Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/strategy.png) |
![Military Aviation Historical Topics Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/history.png)
|
![Information Warfare / Operations and Electronic Warfare Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/iw.png) |
![Systems and Basic Technology Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/technology.png) |
![Related Links Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/links.png) |
|||||||
![Homepage of Australia's First Online Journal Covering Air Power Issues (ISSN 1832-2433) [Click for more ...]](APA/apa-analyses.png) |
|||||||||||||
| Artwork, graphic design, layout and text © 2004 - 2014 Carlo Kopp; Text © 2004 - 2014 Peter Goon; All rights reserved. Recommended browsers. Contact webmaster. Site navigation hints. Current hot topics. | |||||||||||||
|
Site Update
Status:
$Revision: 1.753 $
Site History: Notices
and
Updates / NLA Pandora Archive
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Tweet | Follow @APA_Updates | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
![F-111 Aardvark Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/f-111.png)
![F/A-18 Hornet and Super Hornet Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/fa-18a.png)
![Aerial Refuelling and Airlift Capabilities Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/aar-lift.png)
![Directed Energy Weapons and Electromagnetic Bombs Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/dew.png)
![Notices and Updates Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notices-128.png)
![APA NOTAM and Media Release Index Page [Click for more ...]](APA/notams-128.png)
![APA Research Activities and Policy / Technical Reports Index [Click for more ...]](APA/research-128.png)
![Search Air Power Australia Website [Click for more ...]](APA/search-128.png)
![Briefings and Submissions - Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/briefs-128.png)
![Air Power Australia Contacts [Click for more ...]](APA/contacts-128.png)
![Funding Air Power Australia [Click for more ...]](APA/funding-258.png)